High cholesterol, or hyperlipidaemia, is a significant health concern in Singapore, with its prevalence increasing markedly over the past decade. This condition is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases (CVD), which have consistently been among the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in the nation.
Prevalence of High Cholesterol in Singapore
According to the National Population Health Survey 2020, the prevalence of high blood cholesterol among Singaporean adults rose from 25.2% in 2010 to 39.1% in 2020.
This significant increase indicates that nearly two out of five adults in Singapore have elevated cholesterol levels. The survey also highlighted a concurrent rise in hypertension, another critical risk factor for CVD, from 19.8% to 35.5% over the same period.
Factors Contributing to High Cholesterol
Several modifiable and non-modifiable factors contribute to the high prevalence of elevated cholesterol levels in Singapore:
-
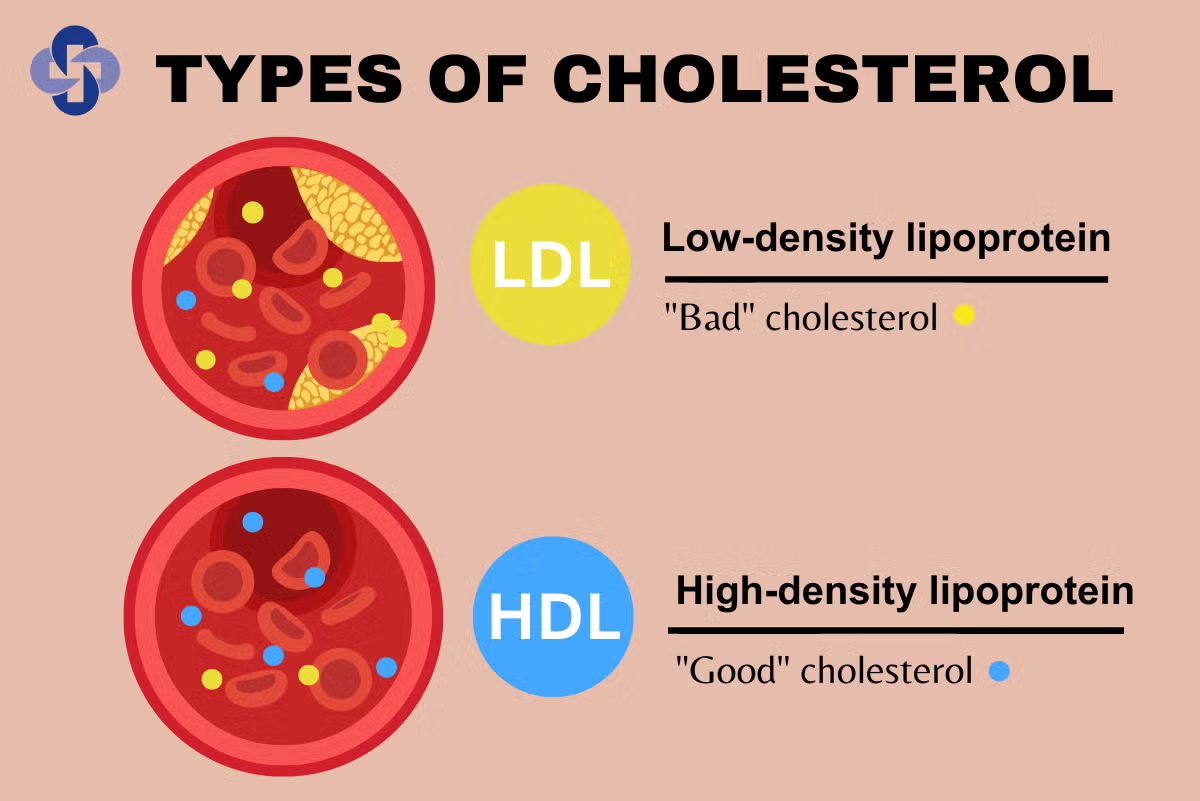
Dietary Habits: Consumption of foods high in saturated and trans fats, such as processed foods, red meat, and full-fat dairy products, can increase low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels.
-
Physical Inactivity: A sedentary lifestyle is associated with lower high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol and higher LDL cholesterol levels, contributing to the risk of hyperlipidaemia.
-
Obesity: Excess body weight is linked to higher total cholesterol, increased LDL cholesterol, and elevated triglyceride levels.
-
Smoking and Alcohol Consumption: Smoking can lower HDL cholesterol and damage blood vessels, while excessive alcohol intake can raise total cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
-
Age and Genetics: Advancing age and a family history of high cholesterol or cardiovascular diseases are non-modifiable risk factors that can predispose individuals to hyperlipidaemia.
Health Implications
Elevated cholesterol levels are a primary contributor to atherosclerosis, a condition characterized by the buildup of fatty deposits in arterial walls. This buildup can lead to narrowed or blocked arteries, increasing the risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease. The rising prevalence of high cholesterol in Singapore correlates with the sustained burden of cardiovascular diseases in the country.
Management and Prevention Strategies
Addressing high cholesterol involves a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle modifications and, when necessary, medical interventions:
-
Dietary Modifications:
- Reduce Saturated and Trans Fats: Limiting intake of foods high in these fats can help lower LDL cholesterol levels.
- Increase Fiber Intake: Consuming more fruits, vegetables, and whole grains adds soluble fiber to the diet, which can reduce cholesterol absorption.
-
Regular Physical Activity:
- Engaging in at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week can help raise HDL cholesterol and lower LDL cholesterol.
-
Weight Management:
- Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight can positively influence cholesterol levels and overall cardiovascular health.
-
Smoking Cessation and Moderation of Alcohol Intake:
- Quitting smoking can improve HDL cholesterol levels, and moderating alcohol consumption can prevent increases in total cholesterol and triglycerides.
-
Regular Health Screenings:
- Routine monitoring of cholesterol levels is crucial for early detection and management of hyperlipidaemia. Individuals aged 40 and above, or those with risk factors, are especially encouraged to undergo regular screenings.
-
Medication:
- For individuals who do not achieve target cholesterol levels through lifestyle modifications alone, healthcare providers may prescribe lipid-lowering medications such as statins. These medications help reduce LDL cholesterol and overall cardiovascular risk.
Public Health Initiatives
In response to the escalating prevalence of high cholesterol and its associated health risks, Singapore has implemented various public health initiatives aimed at promoting cardiovascular health:
-
National Heart Week/World Heart Day: Organized by the Singapore Heart Foundation, this annual event raises awareness about heart health through educational programs, health screenings, and community activities.
-
Health Promotion Campaigns: The Health Promotion Board (HPB) conducts campaigns encouraging healthy eating, regular physical activity, and smoking cessation to address modifiable risk factors associated with high cholesterol.
-
Community-Based Programs: Initiatives such as community health screenings and fitness programs are designed to make preventive healthcare accessible and to encourage healthy lifestyle choices among residents.
Conclusion
The rising prevalence of high cholesterol in Singapore is a pressing public health concern that necessitates comprehensive strategies encompassing individual lifestyle changes, community support, and healthcare interventions. By addressing both modifiable and non-modifiable risk factors, and through sustained public health efforts, it is possible to mitigate the impact of hyperlipidaemia and reduce the burden of cardiovascular diseases in Singapore.
References
-
Singapore Heart Foundation. (n.d.). High Blood Cholesterol. Retrieved from
-
SingHealth. (n.d.). Cholesterol: LDL, HDL & Management. Retrieved from
-
Ministry of Health Singapore. (2022, September 17). Speech by Dr Janil Puthucheary at National Heart Week/World Heart Day 2022.
Leave a Reply